Appended Note 3-1 Dependent population ratio of the consumption base
- Japanese
- English
Concerning the dependent population ratio, we use the dependent population ratio adjusted by weightings of consumption expenditures in view of needs of each age group as the "dependent population ratio of the consumption base."
Consumption expenditures are categorized into "private consumption expenditure," "public education expenditure," "medical insurance benefits" and "nursing care insurance benefits" from the viewpoint of consumption expenditures (including transfers in kind) individuals make in day-to-day living, and consumption expenditures by age group are weighted as in the following table.
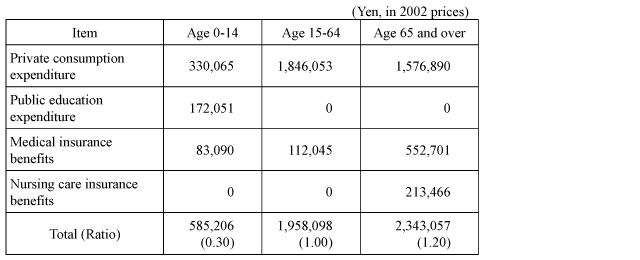
1. Private consumption expenditure
Data was prepared from the 1999 National Survey of Family Income and Expenditure.
All expenditures were converted into 2002 prices using the Consumer Price Index.
(1)Method of preparing data for children aged 14 or under
- Households with children aged 14 or under are assumed to have household heads aged 39 or under.
- Consumption expenditure per child was assumed from the difference in consumption expenditure between households comprising husbands and wives alone and households of husbands, wives and one child each.
- Disposable income was adjusted for households of husbands and wives alone and households of husbands and wives with one child each, and consumption expenditure was calculated from their respective propensity to consume.
- Consumption expenditure related to housing was excluded from consumption expenditure because there is a discrepancy in the ratio of home owners between households of two and households of three, including a child.
(2)Method of preparing data for people aged 15-64
- We assumed that households comprising people within these age groups are represented by single-person households, households of husbands and wives alone, and households of husbands, wives and one child each.
- Consumption expenditure for single-person households was obtained by subtracting expenditure by households of single members aged 65 or over from total expenditure by all single-person households.
- Consumption expenditure for households of husbands and wives alone was obtained by subtracting expenditure by households of elderly husbands and wives from total expenditure by all households of husbands and wives.
- Households of husbands and wives with one child each were divided into households with junior high school children or younger and households with senior high school students. Consumption expenditure for households with junior high school children was obtained by subtracting expenditure by children aged 14 or lower from expenditure of households of husbands and wives with one child reach, and per-capita consumption expenditure was calculated from this data.
- Per-capita consumption expenditure for households with senior high school children was obtained by dividing total expenditures by the total number of people in such households.
- Consumption expenditure for age groups 15-64 was obtained by adjusting expenditures of these three household types by the distribution of households.
(3)Method of preparing data for people aged 65 or over
- Households of people aged 65 or over were assumed to be households of elderly husbands and wives and households of single members aged 65 or over.
- Per-capita consumption expenditure by households of elderly husbands and wives was obtained by dividing total expenditures by the total number of household members.
- Per-capita consumption expenditure by households of single members aged 65 or over was obtained based on the household distribution by each age.
2. Public education expenditure
 Per-capita public education expenditure was estimated by dividing expenditure items considered to be related to compulsory education under the FY2002 budget of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology by the population of children aged 15 or under taken from the Population Estimates of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
Per-capita public education expenditure was estimated by dividing expenditure items considered to be related to compulsory education under the FY2002 budget of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology by the population of children aged 15 or under taken from the Population Estimates of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
3. Medical insurance benefits
 Medical expenditure for each age group was obtained from the National Medical Expenses for 2002 of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Out-of-pocket medical expenses were estimated from the total medical expenses and excluded from medical insurance benefits.
Medical expenditure for each age group was obtained from the National Medical Expenses for 2002 of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Out-of-pocket medical expenses were estimated from the total medical expenses and excluded from medical insurance benefits.
4. Nursing care insurance benefits
 We assumed people receiving nursing care services are all aged 65 or over, and data on per-capita nursing care insurance benefits were obtained by dividing total nursing care insurance benefits announced by the All-Japan Federation of National Health Insurance Organizations by the total number of population aged 65 or over.
We assumed people receiving nursing care services are all aged 65 or over, and data on per-capita nursing care insurance benefits were obtained by dividing total nursing care insurance benefits announced by the All-Japan Federation of National Health Insurance Organizations by the total number of population aged 65 or over.
