Appended Note 2-2 Results of Estimation of Main Banks' Profit Stabilizing Function
- Japanese version
- English version
1. Outline
An analysis is made on how the main bank performs its income stabilizing function (function of stabilizing corporations' ordinary profits by adjusting interest payment burdens) in accordance with the financial conditions of corporate borrowers.
2. Data
Source: Corporate Finance Databank, Development Bank of Japan First half of the 1990s: Average of five-year business results from 1990 to 1994 Second half of the 1990s: Average of five-year business results from 1995 to 1999 *Business results for 1990 mean business results for the period from January to December 1990.
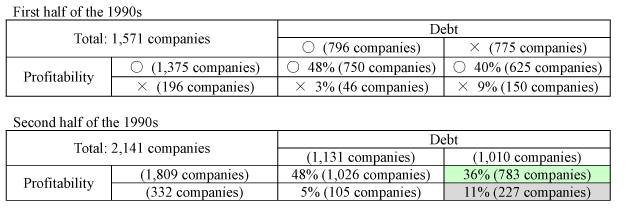
3. Classification of corporations
The ordinary profit-stabilizating function for normal corporations and the one for financial crisis corporations were separated from each other. As to financial crisis corporations, corporations whose debt ratio is above the industry average is defined as "debt increasing corporations" and those whose interest coverage ratio (operating profits / interest payments) is below 1 as "income deteriorating corporations."
Debt 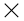 denotes debt increasing corporations, debt
denotes debt increasing corporations, debt 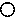 denotes other corporations, and profitability
denotes other corporations, and profitability 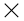 denotes income deteriorating corporations and profitability
denotes income deteriorating corporations and profitability  denotes other corporations.
denotes other corporations.
Their breakdown is as follows:
4. Estimation method
The financial institution whose loan ratio to a given company is the largest was defined as the main bank for the company. The analysis period was divided into two periods-the first half of the 1990s and the second half of the 1990s. Then, an analysis was made on how the relations between listed companies' interest payments and operating profits change depending on the loan ratio of the main bank (loans from main bank / interest-bearing debts) and the loan ratio of financial institutions, including the main bank (loans from financial institutions / interest-bearing debts). In the case where interest payments increases as profit increases and in the case where interest payments decreases as profit decreases, the financial institution can be said to be performing its profit stabilizing function. (Note) As to data, five-year average values were used for each analysis period in order to curb temporary or accidental volatility of financial data. Since interest payments are affected not only by general interest rate fluctuations but also by the amount of debts, the average contractual interest rate multiplied by interest-bearing debt was added to the explanatory variable in order to remove these impacts. In order to see the profit stabilizing function for the above classified companies, a dummy for each classified companies was used. The estimation equation is as below. Note: An increase in profits may be due to an increase in sales and when increased operating funds are financed by borrowings, interest payments may increase.
<Estimation equation>

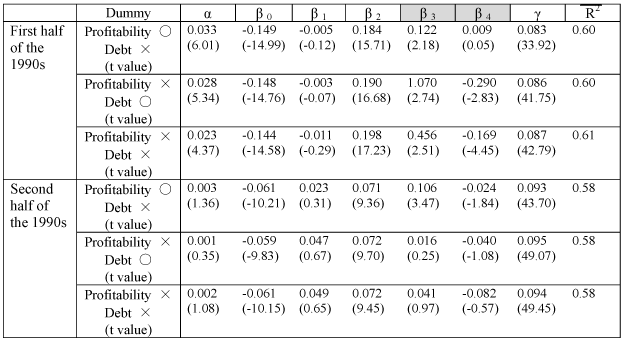
5. Estimate results
It can be said that the main bank in the case of the numerical value of 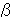 1 being significantly positive, or financial institutions as a whole in the case of the numerical value of
1 being significantly positive, or financial institutions as a whole in the case of the numerical value of 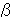 2 being significantly positive are fulfilling their "profit stabilizing function" for corporations other than the dummy corporations.
2 being significantly positive are fulfilling their "profit stabilizing function" for corporations other than the dummy corporations.
It can be said that the main bank in the case of the numerical value of 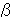 3 being significantly positive, or financial institutions as a whole in the case of the numerical value of
3 being significantly positive, or financial institutions as a whole in the case of the numerical value of 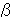 4 being significantly positive are fulfilling their "profit stabilizing function" for the dummy corporations.
4 being significantly positive are fulfilling their "profit stabilizing function" for the dummy corporations.