Appended Note 1-7 VAR Analysis of Japanese and US Interest Rates
- Japanese
- English
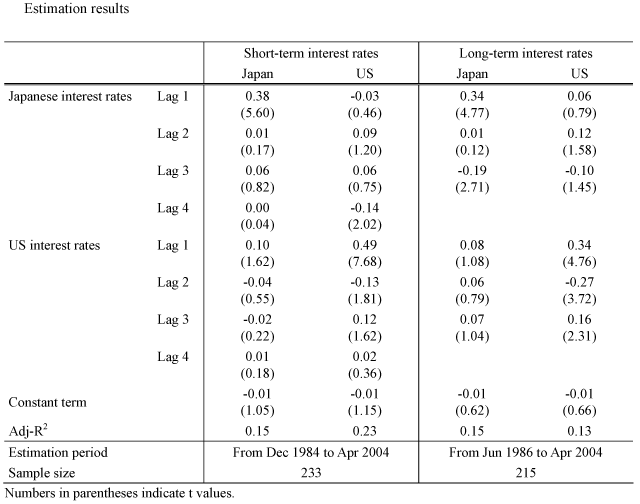
A VAR for Japanese and US short-term interest rates as well as a VAR for Japanese and US long-term interest rates were estimated, and the cumulative impulse response function was used to analyze the impact of a US interest rate shock on Japanese interest rates.
Yields on three-month CDs and ten-year government bonds for Japanese short-term and long-term interest rates respectively, and three-month TBs and ten-year government bonds for US short-term and long-term interest rates respectively, were used. While the results of the ADF test cannot rule out the hypothesis that a unit root in terms of level exists for all Japanese and US short-term as well as long-term interest rates, they can rule out the hypothesis of a unit root existing in terms of difference. As a result, the difference between both short- and long-term interest rates were used to estimate a VAR. The number of lags was chosen four and three for short-term and long-term interest rates respectively based on AIC.
If the number of lags is four for long-term interest rates, same as for short-term interest rates, the 95% confidence interval for the cumulative impulse response function would be greater than zero.