Appended Note 1-2 Stochastic Method for Structural Unemployment Rate
- Japanese
- English
When the number of vacancies and the number of unemployed workers are the same, the labor market can be viewed as balanced and we consider the unemployment rate at such a time as the structural unemployment rate. A cyclical unemployment rate is the unemployment rate (real) minus the structural unemployment rate.
Workers include employees and the self-employed/family employees.
However, in labor supply-demand analyses, the ratio of the unemployed, excluding the self-employed and family employees, to total workforce minus the self-employed and family employees (this is called "employment-unemployment rate" ) is sometimes used. Total workforce minus the self-employed and family employees technically equals the unemployed plus the number of employees.
The number of vacancies is defined not by the number of job offers but by the effective job offers minus cases of employment. This plus the number of employees is employment demand and the vacancy rate is the ratio of the number of vacancies to employment demand.
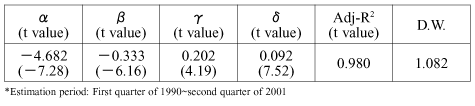
The relationship between the employment unemployment rate and the vacancy rate forms a curve sloping downward from left to right. This is called UV curve, with U standing for Unemployment and V for Vacancy. Models used in the estimation are as follows:
1nU=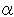 +
+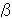
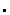 1nV+
1nV+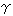
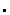 M+
M+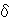
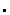 N (UV curve)
N (UV curve)
- U: Employment unemployment rate (=Number of the unemployed/(number of the unemployed+number of employees)x100)
- V: Vacancy rate (=(number of effective job offers--cases of employment)/ {(number of effective job offers--cases of employment)+number of employees}x100)
- M: Of the workers wishing to change jobs, the ratio of those who are actually seeking jobs
- N: Ratio of workers employed in the tertiary industry
If structural employment unemployment rate is U*, structural
unemployment is X, and number of employees is Y, then
1nU*=(1nU-
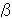
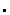 1nV ) / (1-
1nV ) / (1- )
X = Y / (100-U*) x U*
Therefore, if the number of workers is Z, structural unemployment
rate U** is
U** = X / (X + Z) x 100
)
X = Y / (100-U*) x U*
Therefore, if the number of workers is Z, structural unemployment
rate U** is
U** = X / (X + Z) x 100
Estimation result